DeepSeek releases 'DeepSeek-OCR,' a multimodal AI model that uses visual information to compress text input
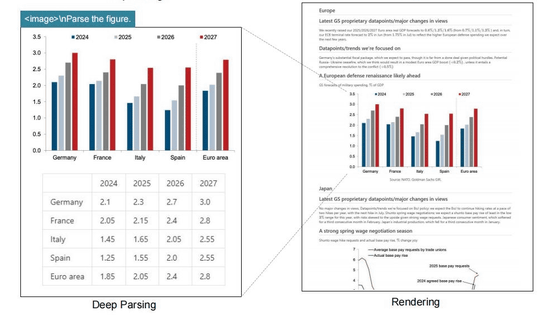
DeepSeek has released a new multimodal AI model called ' DeepSeek-OCR .' 'OCR' stands for Optical Character Recognition, which is used for document scanning and other purposes. The model is said to be able to process large, complex documents while significantly reducing the number of tokens.
GitHub - deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-OCR: Contexts Optical Compression
DeepSeek unveils multimodal AI model that uses visual perception to compress text input | South China Morning Post
Deepseek's OCR system compresses image-based text so AI can handle much longer documents
https://the-decoder.com/deepseeks-ocr-system-compresses-image-based-text-so-ai-can-handle-much-longer-documents/
'DeepSeek-OCR' is a 6.6GB AI model tuned for OCR, capable of compressing text to one-tenth of its original size while retaining 97% of the original information. The system has two cores: a DeepEncoder with 380 million parameters for image processing and a text generator built on DeepSeek3B-MoE with 570 million active parameters.
DeepEncoder reduces the number of tokens in the recognition data and passes them to a model called CLIP, which links images and text. A 1024x1024 pixel image would normally have 4096 tokens, but DeepEncoder processing reduces it to 256 tokens.
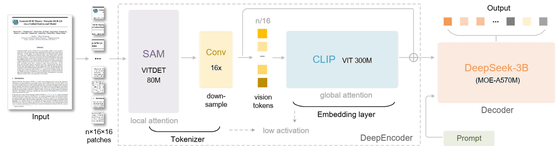
DeepSeek-OCR can operate at a variety of image resolutions, requiring vision tokens ranging from 64 at lower resolutions to up to 400 at higher resolutions. A traditional OCR system performing the same task would require thousands of tokens.
DeepSeek-OCR can process more than 200,000 pages per day using a single NVIDIA A100 GPU, and with 20 servers equipped with eight A100s each, the throughput is said to reach 33 million pages per day.
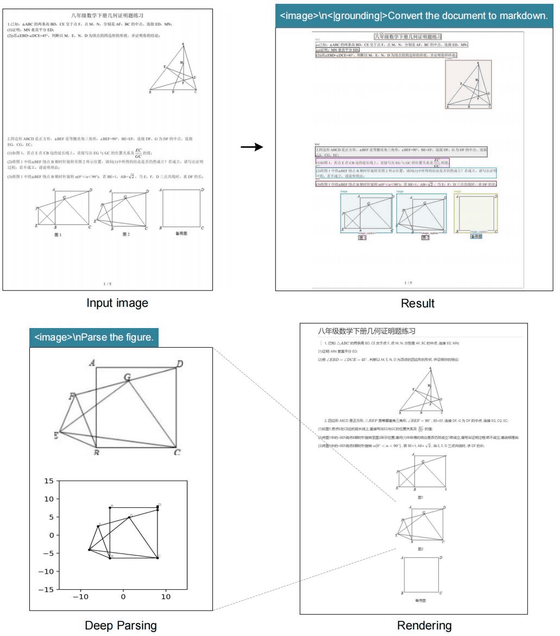
The Hong Kong newspaper South China Morning Post states that DeepSeek-OCR enables users to process ultra-long texts in a scalable manner, retaining the most recent context at high resolution while processing older context with fewer computational resources. This suggests that this opens the door to a theoretically unlimited context architecture that balances information retention and efficiency.
Related Posts:
in AI, Posted by logc_nt