Meta develops a wristband-type device that reads muscle movements and turns them into a keyboard-free input device

On July 24, 2025, Meta announced 'technology that enables mouse operation and keyboard input simply by wearing a wristband and gently moving your wrist and fingers.'
A generic non-invasive neuromotor interface for human-computer interaction | Nature
We're thrilled to see our advanced ML models and EMG hardware — that transform neural signals controlling muscles at the wrist into commands that seamlessly drive computer interactions — appearing in the latest edition of @Nature .
— AI at Meta (@AIatMeta) July 23, 2025
Read the story: https://t.co/7G8qAdnGbh
Find… pic.twitter.com/nEeihClnjv
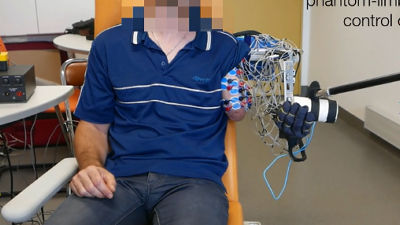
Below is the appearance of the wristband-type device 'sEMG-RD' shown in the paper published in Nature.

In the demo video posted on X, you can see how the sEMG-RD is actually worn.

While wearing the sEMG-RD, you can write letters on a desk by gently moving your finger, and the letters will be entered in accordance with your finger movements.

'With a little practice, you can even move the cursor on your laptop with the right thought,' said Thomas Reardon, Meta's vice president of research. 'You don't have to actually move it, just have the intention to move it.'
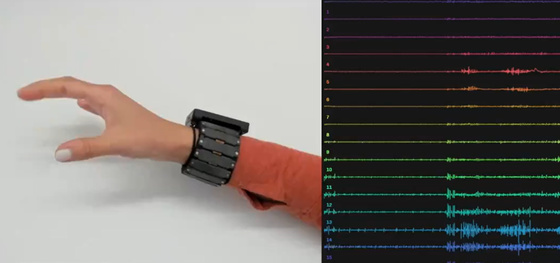
The research team conducted experiments on thousands of subjects and analyzed the data obtained from the experiments with AI to identify common electrical signals that appear when people move their fingers or wrists. The device reads ' electromyograms (EMG) ,' which identify the electrical activity of muscles, and recognizes finger and wrist movements. EMG is powerful, generated by 'alpha motor neurons' that are directly connected to muscle fibers, so it can be read from the outside of the skin with a wristband, without the need for surgicallyimplanting a microchip into the body .
Dario Farina, professor of bioengineering at Imperial College London, said, 'The idea and technology of reading and converting electrical signals with an external device is not new and has been around for decades,' and praised Meta's research for using AI to analyze huge amounts of data from thousands of people and solidify the technology with unprecedented levels of performance.
Reardon said Meta plans to incorporate sEMG-RD's technology into its products within the next few years. Because electromyography was originally studied as a way to control prosthetic hands, the Meta wristband could also be a useful device for people with impaired arm or hand function.
The training data and research models conducted by Meta are publicly available at the following links:
GitHub - facebookresearch/generic-neuromotor-interface: Code for exploring surface electromyography (sEMG) data and training models associated with Reality Labs' paper
https://github.com/facebookresearch/generic-neuromotor-interface
Related Posts: