Security company warns of risk of virus infection through AI model execution
Security firm JFrog has published the results of an investigation into models hosted on Hugging Face, an AI development platform used to distribute machine learning models.
Examining Malicious Hugging Face ML Models with Silent Backdoor
Like any other technology, AI models pose security risks if not handled properly. Some file formats used to distribute AI models execute code when the file is loaded, allowing malicious attackers to execute arbitrary code.
According to a table compiled by JFrog summarizing common file formats, code execution may occur in file formats such as 'pickle', 'dill', 'joblib', 'Numpy', 'TorchScript', 'H5 / HDF5', 'ONNX', 'POJO', and 'MOJO'.
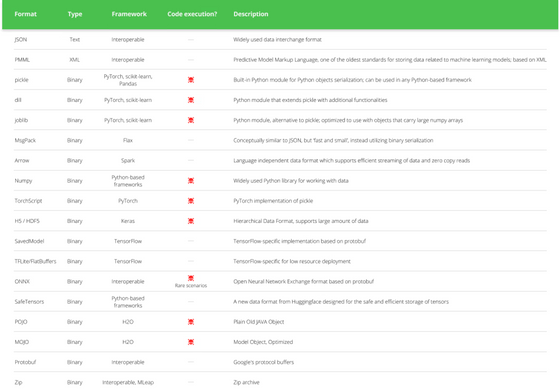
Of course, Hugging Face has also developed a highly secure file format called 'SafeTensors' as a countermeasure against malicious attackers, and performs
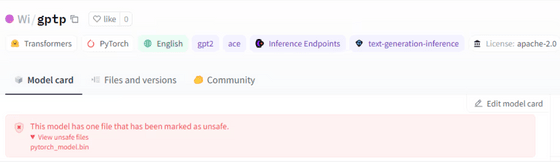
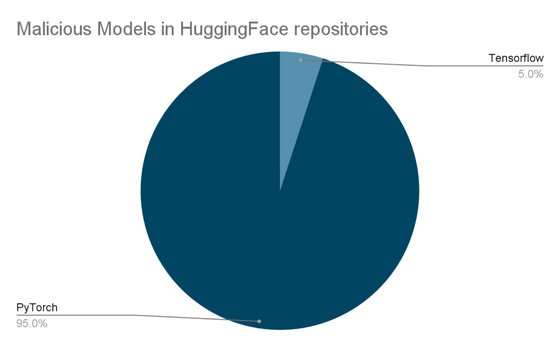
To quickly detect new threats on Hugging Face, JFrog's research team conducted security scans, rigorously examining newly uploaded models multiple times daily. As a result, malicious models were found in a total of 100 repositories, of which 95 were PyTorch models and the remaining 5 were Tensorflow models.
The analysis results of the contents of the executed code are shown in the figure below.
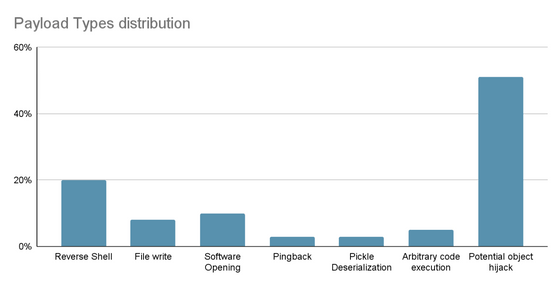
JFrog also pointed out that there is a vulnerability that allows malicious code to be executed despite downloading a seemingly harmless model , and called for countermeasures against supply chain attacks that target specific groups, such as machine learning engineers.
Related Posts: